Varicose veins are a medical issue impacting over thirty percent of the population in India. The prevalence of varicose veins is significantly higher in India compared to many Western nations, with the condition being more common among adults and the elderly.
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted veins that typically appear in the legs. They develop when the valves inside the veins weaken or become damaged, which leads to blood pooling in the veins rather than circulating back to the heart. This pooling causes the veins to bulge, often displaying a bluish or purplish hue. Symptoms associated with varicose veins may include pain and a feeling of heaviness in the legs. There are numerous treatment options available today, ranging from conservative approaches to minimally invasive procedures.
A related condition that people often encounter is spider veins, which bear some resemblance to varicose veins. However, varicose veins are larger, swollen, and painful, while spider veins are small and resemble delicate webs or branches. Typically, spider veins manifest in red, blue, or purple colors and are located closer to the skin’s surface. While varicose veins signify poor blood circulation, spider veins are primarily a cosmetic concern.
Dr. Bhavesh Popat, a vascular and interventional radiologist, states that “Although varicose veins may not pose immediate harm, neglecting them can lead to severe complications such as skin ulcers and blood clots, which significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Therefore, it is crucial to understand their formation for effective management and prevention.”
Varicose veins arise from several factors that damage the valves within the veins, resulting in impaired blood flow. Here are some of the most common causes and risk factors associated with varicose veins:
Family History:
A family history of varicose veins is a significant risk factor. If your parents or other relatives are affected, you are more likely to develop them due to inherited weak vein walls or valves.
Lifestyle Factors:
Prolonged periods of standing or sitting can strain the veins in the legs. A sedentary lifestyle can hinder blood circulation, making it more difficult for veins to return blood to the heart.
Age and Gender:
As people age, their veins may lose flexibility and their valves can sustain damage, raising the likelihood of developing varicose veins. Hormonal changes during pregnancy and menopause also make women more susceptible to this condition.
Other causes of varicose veins include:
Obesity: Excess weight places additional pressure on the veins, forcing them to work harder.
Smoking: This habit damages blood vessels, which results in reduced blood flow to the veins.
Previous injury to a leg or vein increases the risk of developing varicose veins.
Addressing these issues can help prevent the formation of varicose veins and aid in treating existing ones.
Signs and Symptoms of Varicose Veins
Typically, varicose veins present as noticeably swollen veins with a purple or blue hue in the legs. These veins may bulge or twist just beneath the skin, creating an uneven appearance. Additionally, there are other unpleasant symptoms associated with varicose veins:
- Pain and Discomfort: Varicose veins can cause a throbbing sensation or heaviness, particularly after long periods of standing or sitting.
- Swelling: Extended periods of standing may lead to leg and foot swelling, resulting in discomfort and tightness.
- Itch or Burning: Varicose veins can irritate the skin, resulting in itchiness, dryness, or a burning sensation.
- Tired Legs: Often, individuals may experience fatigued, restless, or weak legs due to varicose veins, especially toward the end of the day.
- Cramps or Muscle Spasms: Varicose veins can lead to leg cramps, frequently occurring at night while in bed.
- Skin Discoloration or Ulcers: Severe cases of varicose veins may cause skin discoloration and ulcers.
If varicose veins remain untreated for a prolonged period, the condition may worsen; therefore, early medical intervention is crucial for symptom management. Recognizing these symptoms at an early stage can facilitate effective management of the condition.
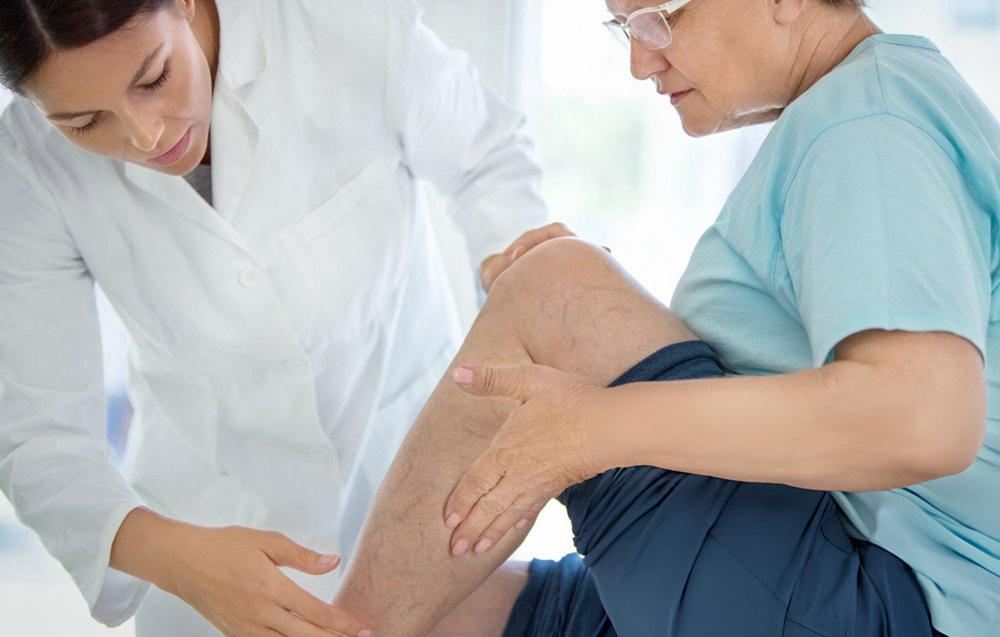
During a physical examination, doctors look for visible swelling and skin changes to diagnose varicose veins. They may recommend ultrasonography to evaluate blood flow and identify any valve defects or blood clots. The seriousness of the condition is determined based on symptom severity, vein size, and other factors, assisting doctors in choosing the best possible treatment.
Tips for the Prevention of Varicose Veins:
- Be Physically Active: Engaging in regular activities such as walking and swimming strengthens the muscles in the legs, thereby reducing pressure on the veins.
- Monitor and Maintain Weight: Excessive weight can strain the veins, increasing the likelihood of varicose vein development.
- Elevate Your Limbs: Regularly raising the legs can enhance blood flow back to the heart.
- Change Positions Regularly: Frequent changes in posture can prevent blood from pooling in the legs during extended sitting or standing.
- Use Compression Stockings: Wearing these can encourage blood circulation in the legs while decreasing vein pressure.
Types of Varicose Vein Treatments Available Today:
The appropriate treatment is based on the severity of the condition and the patient’s overall health.
- Adopt a Healthy Lifestyle: Mild varicose vein symptoms can often be managed with regular exercise, weight management, leg elevation, and the use of compression stockings to relieve symptoms and prevent progression.
- Sclerotherapy: This treatment involves injecting a solution into the affected vein, causing it to collapse and fade over time. It primarily targets small varicose veins and spider veins.
- Endovenous Laser Therapy (EVLT): A modern and effective treatment, EVLT employs laser energy to seal off problematic veins. This minimally invasive method compresses and closes the vein using heat from the laser.
- Vein Stripping and Ligation: This invasive surgery involves tying off and removing problematic veins and is reserved for severe cases.
Each of these treatment options has its unique benefits and downsides. Consulting a medical expert is essential to determine the best treatment suited to your specific circumstances and the severity of your varicose veins.

Leave a Reply